Most computers now come with multiple ports for connecting the computer to external devices. These interfaces and the connectors used have changed over the years and it is difficult for the average computer user to keep abreast of these changes. Here is a quick primer to help you understand these different ports and the devices that you can connect to them.
The USB port
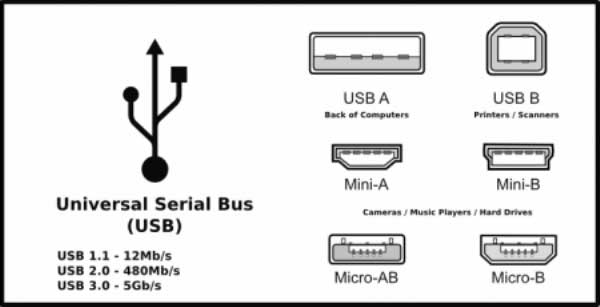
From the early 2000s, the Universal Serial Bus or USB has become the most commonly used port for connection of external devices to the computer. These include the mouse, the keyboard, printers, external hard disk drives, the VOIP phone, the digital camera and a host of other devices. Most computers now provide 3 to 5 USB ports built into the computer and hardware makers have come up with USB extenders that enable even more devices to be connected.
The present version of the port is the USB 2.0 which permits data transfer at 480 Mbps. A newer version, the USB3.0 has been introduced in 2010 and is making its appearance in new computers. This will permit faster data transfers at 5 Gbps. The USB 3.0 port will be backward compatible, accepting USB 2.0 connectors, though with reduced data transfer speeds.
Mini and Micro USBs have been designed for fitment on smaller devices like smartphones and tablets. These are connected to the USB 2.0 or 3.0 port through a connecting cable that has the standard connector at one end and the mini or micro connector at the other.
The advent of the wireless mouse and keyboard and wi-fi connections to printers has reduced pressure on the number of USBs occupied on the computer. There is however increased use of computer USB ports as the power source to charge mobile phones and tablet computers to save in carrying the bulky charger units.
The Ethernet jack
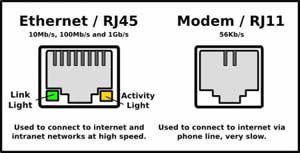 The Ethernet RJ 45 jack is still the most popular means of connection of the internet modem to the computer. Though wi-fi networks are becoming more common at the workplace and even at home, the main home or workplace computer is typically connected with an Ethernet cable. Data speeds up to 100 Mbps are possible with the Ethernet and the connection is by a cable not exceeding 100 meters in length between the modem and the computer.
The Ethernet RJ 45 jack is still the most popular means of connection of the internet modem to the computer. Though wi-fi networks are becoming more common at the workplace and even at home, the main home or workplace computer is typically connected with an Ethernet cable. Data speeds up to 100 Mbps are possible with the Ethernet and the connection is by a cable not exceeding 100 meters in length between the modem and the computer.
Newer Gigabit Ethernet technology is just emerging that would permit data transfer speeds to increase 10 times to 1 Gbps.
The Video Connectors
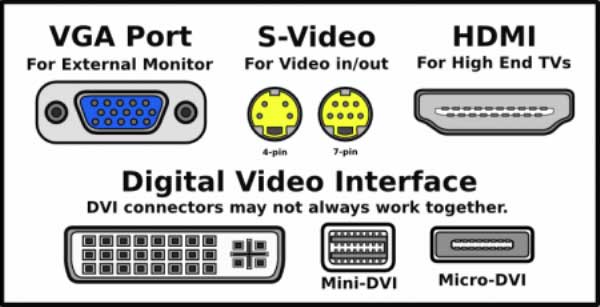 The Video Graphics Array (VGA) port is used to connect an external monitor to the computer. Laptop computers often have a relatively small display screen that is uncomfortable to use for prolonged periods. The VGA port is used to connect an external large LCD screen. The connection to the larger monitor also permits sharing of desktop screens in meeting rooms.
The Video Graphics Array (VGA) port is used to connect an external monitor to the computer. Laptop computers often have a relatively small display screen that is uncomfortable to use for prolonged periods. The VGA port is used to connect an external large LCD screen. The connection to the larger monitor also permits sharing of desktop screens in meeting rooms.
The High Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) permits uncompressed audio and video signals to be connected to the computer. The external devices typically connected through an HDMI port include a DVD or Blueray disc player, a Camcorder or a gaming console like Xbox or PlayStation.
Prior to the HDMI interface, the Digital Video Interface was used for such connections and would often have compatibility problems between the external device and the computer.
Audio connectors
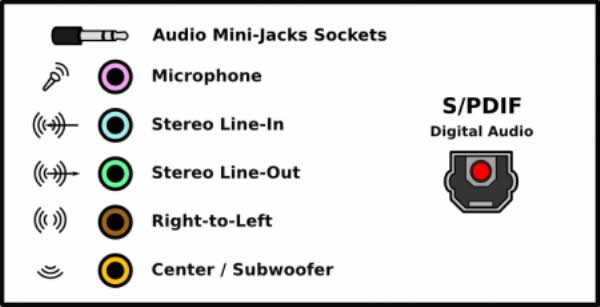 Audio connectors, as the name suggests, is to connect external speakers to the computer. The analog output jacks are color-coded as shown above and the same colors are used on the speaker connection jacks. The analog ports include a connector for microphone input into the computer.
Audio connectors, as the name suggests, is to connect external speakers to the computer. The analog output jacks are color-coded as shown above and the same colors are used on the speaker connection jacks. The analog ports include a connector for microphone input into the computer.
The analog connection is being replaced with the S/P DIF digital connector which stands for Sony/Philips Digital Interconnect Format. This digital port permits the computer to become interconnected to a home theater system. The interconnection is by coaxial copper cables or in high performance systems with fiber optic cables.
Power connectors
 These are comparatively easier to identify and are the ports for plugging in the mains power chord to the computer. Most computers now accept 120 / 220 volt input so that the computer is usable either in the US or in other parts of the world without needing a step down transformer.
These are comparatively easier to identify and are the ports for plugging in the mains power chord to the computer. Most computers now accept 120 / 220 volt input so that the computer is usable either in the US or in other parts of the world without needing a step down transformer.
Other ports
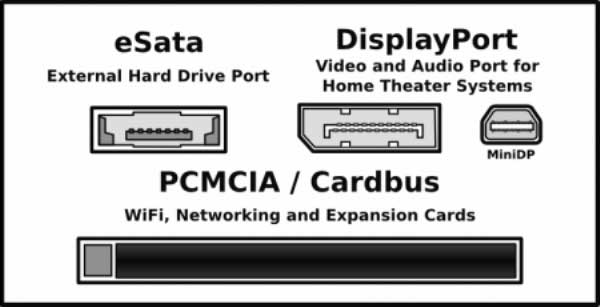 Computers could also be fitted with various other kinds of ports for specific functions. The eSata port connects to external data storage devices like hard disks or optical drives. The advantage over the USB 2.0 is that data transfer speeds are three times faster but the port does not provide power to the external drive that has to be independently powered through built-in batteries or by a separate connection to the mains.
Computers could also be fitted with various other kinds of ports for specific functions. The eSata port connects to external data storage devices like hard disks or optical drives. The advantage over the USB 2.0 is that data transfer speeds are three times faster but the port does not provide power to the external drive that has to be independently powered through built-in batteries or by a separate connection to the mains.
The DisplayPort has been developed by the Video Electronics Standards Association as an alternative to the HDMI which charges a royalty. It is based on new technology that can shift allocation of bandwidth between video and audio signals seamlessly and improve data transmission speeds. For the near future, computers may have both HDMI and DipslayPort connectors until the market place decides the preferred technology.
The PCMCIA or Cardbus slot is provided in many computers to accept an external memory storage device or for a wireless network connection card for mobile phone or internet access. These are now being replaced by dongles that fit into USB ports.
 Computers are fitted with multiple ports that serve different functions. These can cause doubts and confusion in the minds of the average user particularly due to the use of an alphabet soup of acronyms by the industry. One fortunate part of this variety is that the connectors are not interchangeable and you cannot plug in a wrong device into a port. The USB 2.0 port has become the preferred interconnection port for most devices that you may want to connect to the computer and that has the advantage of also providing the power supply to the connected device.
Computers are fitted with multiple ports that serve different functions. These can cause doubts and confusion in the minds of the average user particularly due to the use of an alphabet soup of acronyms by the industry. One fortunate part of this variety is that the connectors are not interchangeable and you cannot plug in a wrong device into a port. The USB 2.0 port has become the preferred interconnection port for most devices that you may want to connect to the computer and that has the advantage of also providing the power supply to the connected device.

